Steel is ubiquitous, appearing in construction sites, car manufacturing plants, and even in the production of household appliances.
However, with the variety of steel products available, many technical staff are puzzled about which type to select: hot-rolled or cold-rolled steel. In China, approximately 75% of steel manufacturers operate hot-rolled and cold-rolled production lines, yet 30% of end users incur unnecessary expenses due to poor choices.
This article will deeply analyze the essential differences between the two processes, provide a scenario-based selection guide, and reveal the industry’s cutting-edge technologies to help you say goodbye to material selection anxiety.
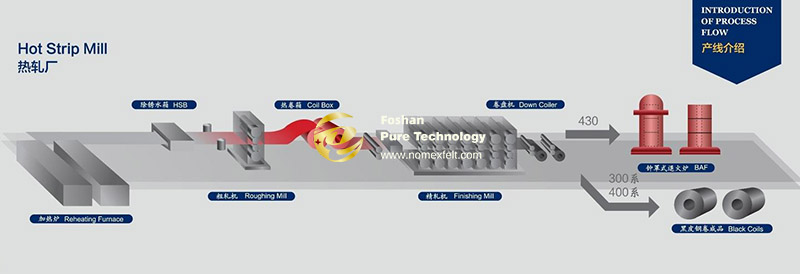
The hot rolling process of steel encompasses five distinct stages: preparation of raw materials, heating, rolling, cooling, and finishing. Each link involves complex process parameter control and equipment coordination.
The steel billets coming out of the steel mill are only semi-finished products. They must be rolled in the steel rolling mill before they can become qualified products.
The continuous casting billets sent from the steel mill first enter the heating furnace, and then enter the finishing mill after repeated rolling in the primary rolling mill. On the hot rolling production line, the billets are heated and softened, sent to the rolling mill by rollers, and finally rolled into the size required by the user.
The hot-rolled finished products are divided into two types: steel coils and ingot plates. The thickness of the hot-rolled rail is generally several millimeters. If the user requires a thinner steel plate, it must also be cold rolled.
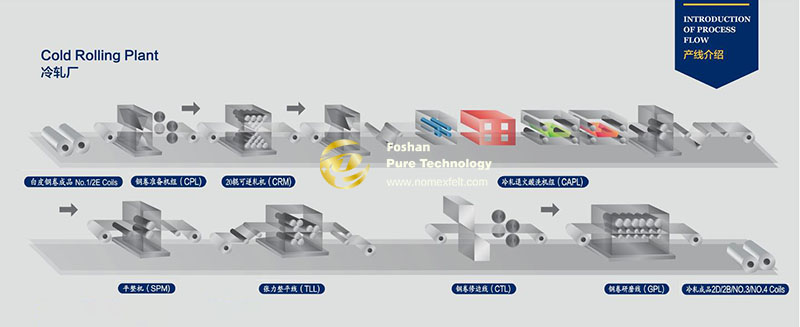
Compared with hot rolling, the cold rolling process of steel needs to go through seven stages: raw material preparation, pickling, cold rolling, annealing, cutting, surface treatment, testing, and packaging.
The cold rolling mill’s processing lines are relatively scattered. The steel coils sent from the hot rolling mill must first undergo three consecutive technical treatments.
The oxide film must be removed with hydrochloric acid before they can be sent to the cold rolling unit.
On the cold rolling mill, the unwinder opens the steel coil, and then the steel strip is introduced into the five-stand continuous rolling mill to be rolled into a thin strip coil.
During the cold rolling process, the steel is further reduced in thickness and improved in dimensional accuracy and surface quality through the extrusion of the rollers at room temperature.
Because cold rolling is carried out at a lower temperature, the work hardening phenomenon of the steel is more obvious, and intermediate annealing and other treatments are required to restore its plasticity.
The cold-rolled materials are cut to the corresponding size according to customer needs. Cutting can be done with shears, steel strip cutters, and other tools.
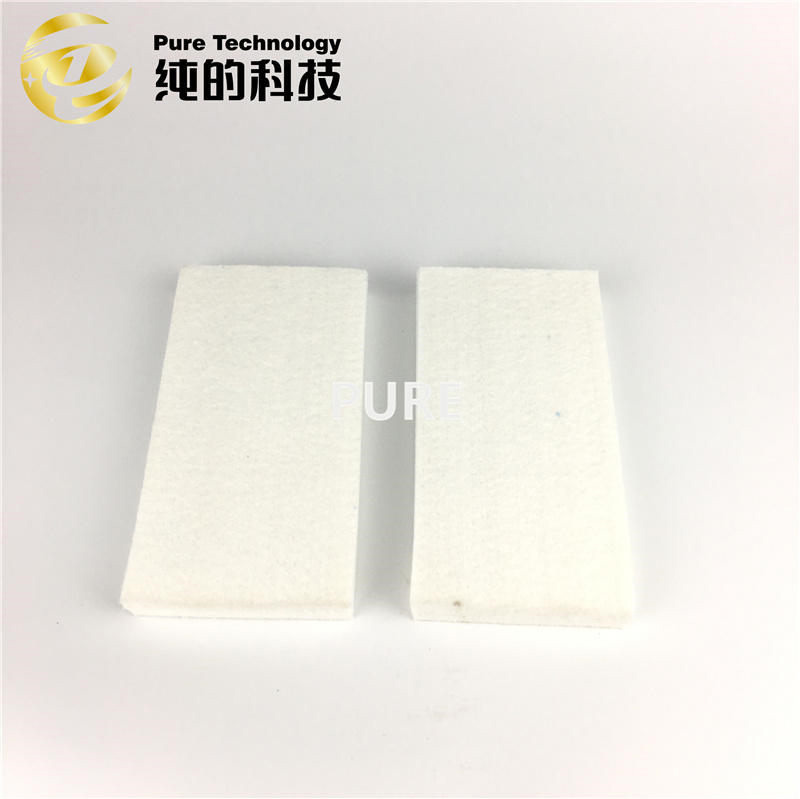
The rolled steel felt is the core component of the steel strip cutter, which is responsible for controlling the tension of the steel strip and protecting the surface quality during the cutting process. Its role runs through the entire cutting process.
Before cutting, confirm that the felt tension pad is free of defects and contamination, select the tension pad length according to the width of the steel strip, and adjust the thickness according to the steel strip parameters.
Damping vibration: ensure the accuracy of cutting a straight line and avoid the deviation of cutting caused by vibration (±0.1mm tolerance control).
Surface protection: Prevent the steel strip from being scratched through flexible contact and maintain the surface finish after cold rolling.
Friction optimization: reduce the friction coefficient between steel strip and equipment (μ≤0.15) and extend the tool life.

|
Factor |
Hot Rolling |
Cold Rolling |
|
Temperature |
1100℃~1250℃ |
Normal temperature |
|
Surface roughness |
Rough (needs post-processing) |
Smooth (ready to use) |
|
Dimensional accuracy |
±0.1-0.2 mm |
±0.02-0.05 mm |
|
Strength |
Lower |
High |
|
Cost |
Low (no secondary processing required) |
High (complex process) |
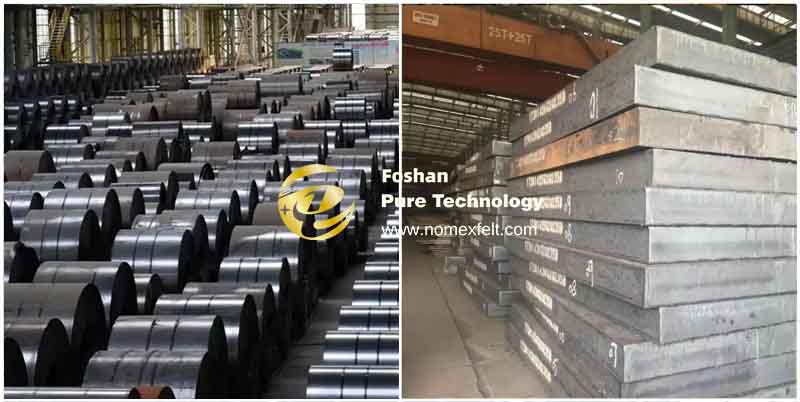
Raw materials: Hot rolled steel plate is made from slab (mainly continuous casting slab) as raw material, which is made into strip steel by rough rolling unit and finishing rolling unit after heating; cold rolled steel plate is made from hot coil as raw material, which is rolled below the recrystallization temperature at room temperature.

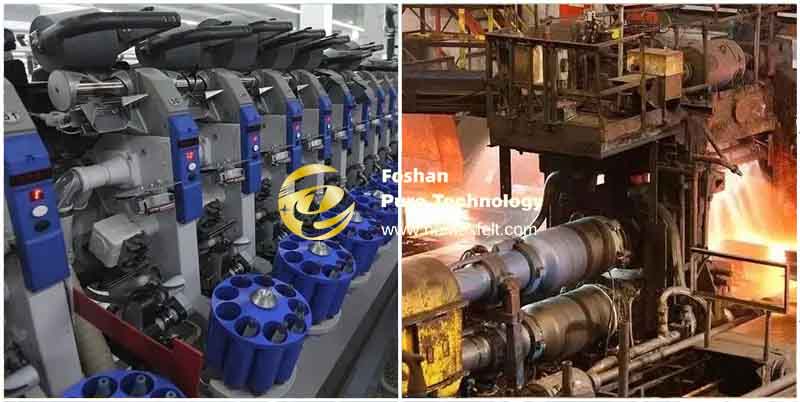
Equipment requirements: Hot rolling equipment is usually large, including heating furnaces, roughing mills, finishing mills, etc. This equipment needs to withstand high temperatures and high pressures to meet the requirements of the hot rolling process.
Cold rolling equipment is usually more sophisticated, including cold rolling mills, skin pass mills, etc. They need to have high precision and high rigidity to ensure product quality.

Appearance and surface quality: Cold rolled products have higher dimensional accuracy and can be controlled within a smaller tolerance range. This is because the cold rolling process uses sophisticated equipment and processes to control the thickness, width, and other dimensions of the product.
Hot rolled products are prone to deformation because the metal material is rolled at high temperatures during the hot rolling process, so the dimensional accuracy is relatively low, and the tolerance range is also large.
Mechanical properties: The mechanical properties of cold rolling are usually better than those of hot rolling.
Because the work hardening effect or cold work hardening produced during the cold rolling process results in higher surface hardness and strength of cold-rolled plates, but lower toughness.
While the mechanical properties of hot-rolled plates are far inferior to those of cold-rolled plates, they have better toughness and ductility.
Surface Quality: The quality of the surface structure of cold rolled steel will be better than that of hot rolled steel. Cold rolled products are harder and less ductile, while hot rolled products have a rougher, textured surface.
Fast forming speed, high output, no damage to the coating, can be made into a variety of cross-sectional forms to meet the needs of use conditions. Cold rolling can cause great plastic deformation of steel, thereby increasing the yield point of steel.
It can destroy the casting structure of the steel ingot, refine the grains of the steel, and eliminate the defects of the microstructure so that the steel structure is dense and the mechanical properties are improved.
This improvement is mainly reflected in the rolling direction so that the steel is no longer isotropic to a certain extent; the bubbles, cracks, and looseness formed during pouring can also be welded under high temperature and pressure.
The local strain induced by weld shrinkage often reaches several times the yield point strain, which is much larger than the strain caused by the load;
Hot-rolled steel sections of various cross-sections have this type of residual stress. Generally, the larger the cross-sectional size of the steel section, the greater the residual stress.
Although residual stress is self-balanced, it still has a certain impact on the performance of steel components under external forces, such as deformation, stability, and fatigue resistance.
Hot rolled steel coils are widely used in construction, bridges, ships, machinery manufacturing, and other fields. For example, patterned plates, beam steel, boom steel, etc., are mostly manufactured using hot rolling technology.
Cold rolled steel coils are mainly used to manufacture parts for automobiles, home appliances, electronic products, etc., that require high dimensional accuracy and surface quality.
Lechler technology
SCALEMASTER nozzle: When hot rolling steel, the surface quality of the rolled material depends largely on the descaling effect.
To avoid surface damage of the rolled material, high-pressure water jets are required to remove the iron oxide scale in the process from hot billet to hot rolling coiling. It is very important to select superior descaling nozzles and arrange them optimally.
At present, the hot rolling process technology level cannot prevent the steel plate surface from being oxidized during the hot rolling process, nor can it completely avoid the poor surface quality caused by iron oxide scale.
Therefore, hot rolling is not suitable for producing plate and strip steel products with high surface finish requirements. The surface roughness of the hot-rolled plate is 20μm in the hot-rolled state and 25μm after pickling.
The surface of the cold-rolled plate is clean and bright, and steel plates with different surface roughnesses can be manufactured according to different uses. Such surface quality cannot be met by hot rolling.
Cold-rolled steel is more susceptible to rust than hot-rolled steel in the bare steel state because of its smooth surface and an oxide layer. However, the speed and degree of rusting depend on the following four factors:
Material itself: Cold-rolled steel is essentially carbon steel (containing iron). It will inevitably rust when in contact with water and oxygen without surface treatment.
Surface treatment process (key difference): galvanizing/chrome plating > phosphating > bare steel.Use environment: The rusting rate in the coastal high salt fog environment is 8-10 times that of the dry inland environment.Protection and maintenance: Regular application of anti-rust oil can delay 3-5 years.
Because of the work hardening or cold hardening effect produced during the cold rolling process, the surface hardness and strength of cold-rolled plates are higher, but the toughness is lower.
The mechanical properties of hot-rolled plates are far inferior to those of cold-rolled plates, but they have better toughness and ductility.
Hot rolled steel has excellent properties such as high strength, good toughness, easy processing, and good weldability. Your project prioritizes cost over surface finish.
For example, thick-walled sections (thickness greater than 0.25 inches) are required, or dimensional accuracy is not required (for example, structural frames). Choose hot rolled steel if the following situations occur.
Structural steel frames: Hot rolled I-beams, H-beams, and channels are commonly used in load-bearing structures in building structures.
Bridges: Due to its strength and durability, steel produced by hot rolling is often used to make structural components of bridges.
Railroad tracks: Tracks used for railroad tracks are usually made of hot rolled steel.
Machinery and equipment: Many heavy machinery and equipment components are made of hot rolled steel due to its strength and cost-effectiveness.
Cold-rolled steel is used for its advantages in mechanical properties, surface quality, dimensional accuracy, and processing performance.
If you need tight tolerances and smooth surfaces, your design involves complex shapes (for example, stampings), and if the following situations occur, choose cold-rolled steel.
Building components: Experts often incorporate cold-formed steel sections into their designs for their smooth appearance and precise measurements.
Automotive industry: Cold-formed steel is used in automotive parts where weight reduction and strength are essential.
Storage systems: The precision and strength of cold-formed steel make it widely used in building racks, shelves, and storage systems.
Typically, cold rolling is priced a bit higher than hot rolling. This is due to the need for advanced processing equipment and a more intricate technological process in cold rolling, which also results in superior surface treatment.
Therefore, the quality of cold-rolled products is usually higher, and the corresponding price is also more expensive. In addition, cold-rolled steel requires more stringent processing technology during the production process, the processing is more difficult, and the requirements for production equipment, rollers, and other equipment are higher, which will also lead to an increase in production costs.
Green smart rolling technology is centered on “shortening the process, increasing efficiency through intelligence, and low-carbon circulation” and is driven by both material research and development and process innovation.
The focus is on three major paths: developing high-service-life steel grades to reduce resource consumption, building a full-process digital production system to reduce energy consumption, and developing short-process processes such as composite rolling to achieve energy conservation and emission reduction.
The online composite rolling process of heterogeneous materials is used to break through the process limitations of traditional cladding processes.
Through dynamic temperature field control and interface metallurgical bonding technology, composite plates such as stainless steel/carbon steel can be formed in one go, reducing the intermediate annealing link, increasing the production line efficiency by 30%, and increasing the metal recovery rate to 98.5%.
Based on the deep learning algorithm, a rolling parameter-organization performance mapping model is established. By collecting real-time data (temperature, pressure, speed, etc.) of the production line, the neural network is trained to realize intelligent recommendations for the rolling process.
A multi-source heterogeneous data fusion platform is developed to integrate 2000+ sensor data (including infrared thermal imagers, laser velocimeters, etc.) to build a dynamic early warning mechanism for process windows.
Practical applications show that the response time to abnormal conditions is shortened to 15 seconds, and the dimensional accuracy is improved to ±0.05mm.
Through the practice of digital transformation, the steel plate production line has achieved the following: the process design cycle is shortened by 40%. The efficiency of quality abnormality tracing is improved by 65%; the carbon emission intensity of the rolling process is reduced by 12%. The choice between cold rolled steel and hot rolled steel comes down to a balance of cost, precision, and application needs.
As sustainable practices and smart manufacturing advance, both processes will continue to evolve to meet future engineering challenges.
Need expert advice? Contact us to explore how felt tension pads and precision steel solutions can optimize your production line!
As we know, Heat Transfer Printing Felt is suitable for fabrics, decorative fabrics, curtains, le...
Read Safety Rules for Laundry Management to be a qualified manager. PARTⅠ Laundry room Safety Gen...
The aluminum extrusion machine is the leading equipment for the production of aluminum profiles. ...
Heat transfer printing is a contemporary printing process in the clothing market. It prints the p...
In the textile industry, felt is only a small part but important. About how to choose felt that i...
Foshan Pure Technology Company., Ltd. helps conveyor belt manufacturers source equipment to metal...
Nomex, an intermediate aramid, also known as aramid 1313. It is characterized by good heat resist...
In the 1960s, the Dupont developed a kind of aramid composite material, it is Kevlar. It has very...